02-Peve-reference-annotation
================
Kathleen Durkin
2024-09-04
- 1 Transcriptome
- 1.1 Retrieve transcriptome
fasta file
- 1.2
Database Creation
- 1.2.1 Obtain Fasta
(UniProt/Swiss-Prot)
- 1.2.2 Making the database
- 1.3 Running
Blastx
- 1.4 Joining Blast table
with annoations.
- 1.4.1 Prepping Blast
table for easy join
- 1.4.2
Could do some cool stuff in R here reading in table
Code to annotate our *P. evermanni* reference files (the *P.evermanni*
transcriptome and genome) with GO information
# 1 Transcriptome
## 1.1 Retrieve transcriptome fasta file
We’ll be using the *P. evermanni* genes fasta file constructed using the
*P. evermanni* gff and scaffold fasta, stored
[here](https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/kdurkin1/deep-dive/E-Peve/data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta).
Accessible on the `deep-dive` [genomic resources
page](https://github.com/urol-e5/deep-dive/wiki/Species-Characteristics-and-Genomic-Resources#genomic-resources),
including links to relevant code.
``` bash
curl https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/kdurkin1/deep-dive/E-Peve/data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta \
-k \
> ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta
```
Let’s check the file
``` bash
echo "First few lines:"
head -3 ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta
echo ""
echo "How many sequences are there?"
grep -c ">" ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta
```
## First few lines:
## >Parent=Peve_00000001 Porites_evermani_scaffold_1:3106-3444,4283-4488
## TTACTGCTTCAGTATGTGAATTTCGATGGTGGCTTGACCGGAGTTAGACATGGCCCCCCTTGCTCGGAGTCCCGATCCCAAATCTCTCTCGTGCCAGTAGTTATCTCCTTTGAAGGGATTATCGTAATACATCCGGTACCAAAGATTGTAGTTGGCGCGTCTTTTACCACTGTAAAGCCAAACATCAAACCAGTTGCTGTACCAGTTGTAGTCAAATGGAACGGAATACATAACAGCAAGTGTTTTATCGATGTGTGGGATGTAGTATGTTAATACTCCTACTGCGCCTCTCGCAACGGGCCCCGCAGTTTTTCGTGCGCCGTAAAGCAAAGCTGTGCCTGAAGAAACATCATGAGGCAAAACACGATTTGACGTCCCTGAATAAAAATATATGTTGACTGCTCTCCATTTATATCCACTTTCGTTATCAACACCAATGGCGACCTTGCGGCTTATGCTACCAAGGGTGTTTAAAATTGTTGTGAGAATGCCCAAGCCAAGTTGAGCACCGCTGATGACAGCACCAGCGTCAGCTAAAATTTT
## >Parent=Peve_00000002 Porites_evermani_scaffold_1:424478-425361,426180-426735,427012-427140,427664-427724,428641-429034
##
## How many sequences are there?
## 40389
For simplicity, let’s reduce the sequence names to just the unique
identifier “Parent=Peve\_########”
``` r
# Read FASTA file
fasta_file <- "../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta" # Replace with the name of your FASTA file
sequences <- readDNAStringSet(fasta_file)
# For simplicity, let's reduce the sequence names to just the unique identifier "Parent=Peve_########"
names(sequences) <- gsub("^(Parent=Peve_\\d+).*", "\\1", names(sequences))
head(names(sequences))
```
## [1] "Parent=Peve_00000001" "Parent=Peve_00000002" "Parent=Peve_00000003"
## [4] "Parent=Peve_00000004" "Parent=Peve_00000005" "Parent=Peve_00000006"
``` r
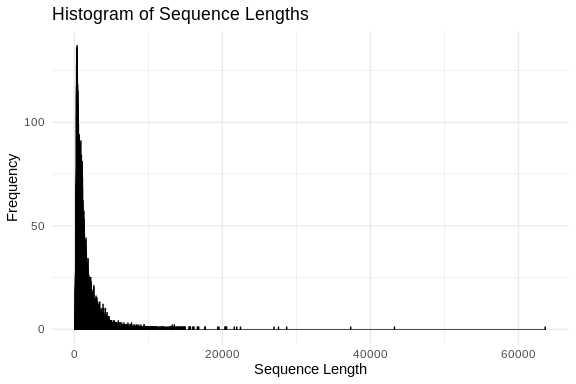
# Calculate sequence lengths
sequence_lengths <- width(sequences)
# Create a data frame
sequence_lengths_df <- data.frame(Length = sequence_lengths)
# Plot histogram using ggplot2
ggplot(sequence_lengths_df, aes(x = Length)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, color = "black", fill = "blue", alpha = 0.75) +
labs(title = "Histogram of Sequence Lengths",
x = "Sequence Length",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal()
```
 ``` r
summary(sequence_lengths_df)
```
## Length
## Min. : 102
## 1st Qu.: 519
## Median : 933
## Mean : 1338
## 3rd Qu.: 1617
## Max. :63597
``` r
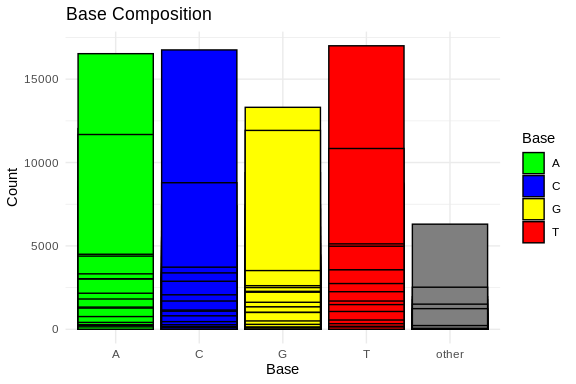
# Calculate base composition
base_composition <- alphabetFrequency(sequences, baseOnly = TRUE)
# Convert to data frame and reshape for ggplot2
base_composition_df <- as.data.frame(base_composition)
base_composition_df$ID <- rownames(base_composition_df)
base_composition_melted <- reshape2::melt(base_composition_df, id.vars = "ID", variable.name = "Base", value.name = "Count")
# Plot base composition bar chart using ggplot2
ggplot(base_composition_melted, aes(x = Base, y = Count, fill = Base)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge", color = "black") +
labs(title = "Base Composition",
x = "Base",
y = "Count") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("A" = "green", "C" = "blue", "G" = "yellow", "T" = "red"))
```
``` r
summary(sequence_lengths_df)
```
## Length
## Min. : 102
## 1st Qu.: 519
## Median : 933
## Mean : 1338
## 3rd Qu.: 1617
## Max. :63597
``` r
# Calculate base composition
base_composition <- alphabetFrequency(sequences, baseOnly = TRUE)
# Convert to data frame and reshape for ggplot2
base_composition_df <- as.data.frame(base_composition)
base_composition_df$ID <- rownames(base_composition_df)
base_composition_melted <- reshape2::melt(base_composition_df, id.vars = "ID", variable.name = "Base", value.name = "Count")
# Plot base composition bar chart using ggplot2
ggplot(base_composition_melted, aes(x = Base, y = Count, fill = Base)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge", color = "black") +
labs(title = "Base Composition",
x = "Base",
y = "Count") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("A" = "green", "C" = "blue", "G" = "yellow", "T" = "red"))
```
 ``` r
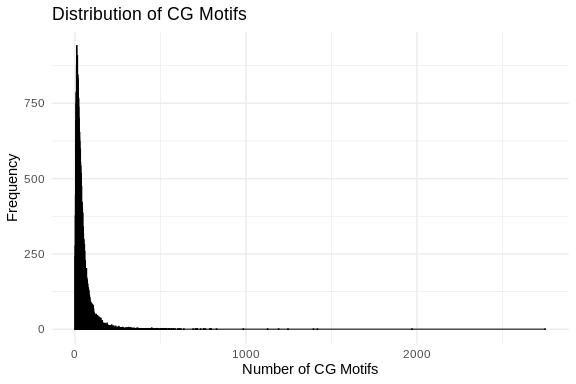
# Count CG motifs in each sequence
count_cg_motifs <- function(sequence) {
cg_motif <- "CG"
return(length(gregexpr(cg_motif, sequence, fixed = TRUE)[[1]]))
}
cg_motifs_counts <- sapply(sequences, count_cg_motifs)
# Create a data frame
cg_motifs_counts_df <- data.frame(CG_Count = cg_motifs_counts)
# Plot CG motifs distribution using ggplot2
ggplot(cg_motifs_counts_df, aes(x = CG_Count)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, color = "black", fill = "blue", alpha = 0.75) +
labs(title = "Distribution of CG Motifs",
x = "Number of CG Motifs",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal()
```
``` r
# Count CG motifs in each sequence
count_cg_motifs <- function(sequence) {
cg_motif <- "CG"
return(length(gregexpr(cg_motif, sequence, fixed = TRUE)[[1]]))
}
cg_motifs_counts <- sapply(sequences, count_cg_motifs)
# Create a data frame
cg_motifs_counts_df <- data.frame(CG_Count = cg_motifs_counts)
# Plot CG motifs distribution using ggplot2
ggplot(cg_motifs_counts_df, aes(x = CG_Count)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, color = "black", fill = "blue", alpha = 0.75) +
labs(title = "Distribution of CG Motifs",
x = "Number of CG Motifs",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal()
```
 ## 1.2 Database Creation
### 1.2.1 Obtain Fasta (UniProt/Swiss-Prot)
``` bash
cd ../../data
curl -O https://ftp.uniprot.org/pub/databases/uniprot/current_release/knowledgebase/complete/uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz
mv uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
gunzip -k uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
```
### 1.2.2 Making the database
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/makeblastdb \
-in ../../data/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta \
-dbtype prot \
-out ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04
```
## 1.3 Running Blastx
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/blastx \
-query ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta \
-db ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04 \
-out ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
-evalue 1E-20 \
-num_threads 20 \
-max_target_seqs 1 \
-outfmt 6
```
``` bash
echo "First few lines:"
head -2 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
echo "Number of lines in output:"
wc -l ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
```
## First few lines:
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp|P61915|ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
## Parent=Peve_00000002 sp|Q569C3|UBP1_RAT 48.000 200 94 5 1287 703 407 601 1.43e-45 177
## Number of lines in output:
## 25243 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
## 1.4 Joining Blast table with annoations.
### 1.4.1 Prepping Blast table for easy join
``` bash
tr '|' '\t' < ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
> ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
head -1 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
```
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp P61915 ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
### 1.4.2 Could do some cool stuff in R here reading in table
``` r
bltabl <- read.csv("../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab", sep = '\t', header = FALSE)
spgo <- read.csv("https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/snaps/uniprot_table_r2023_01.tab", sep = '\t', header = TRUE)
datatable(head(bltabl), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(head(spgo), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(
left_join(bltabl, spgo, by = c("V3" = "Entry")) %>%
select(V1, V3, V13, Protein.names, Organism, Gene.Ontology..biological.process., Gene.Ontology.IDs)
)
```
## 1.2 Database Creation
### 1.2.1 Obtain Fasta (UniProt/Swiss-Prot)
``` bash
cd ../../data
curl -O https://ftp.uniprot.org/pub/databases/uniprot/current_release/knowledgebase/complete/uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz
mv uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
gunzip -k uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
```
### 1.2.2 Making the database
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/makeblastdb \
-in ../../data/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta \
-dbtype prot \
-out ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04
```
## 1.3 Running Blastx
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/blastx \
-query ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta \
-db ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04 \
-out ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
-evalue 1E-20 \
-num_threads 20 \
-max_target_seqs 1 \
-outfmt 6
```
``` bash
echo "First few lines:"
head -2 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
echo "Number of lines in output:"
wc -l ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
```
## First few lines:
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp|P61915|ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
## Parent=Peve_00000002 sp|Q569C3|UBP1_RAT 48.000 200 94 5 1287 703 407 601 1.43e-45 177
## Number of lines in output:
## 25243 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
## 1.4 Joining Blast table with annoations.
### 1.4.1 Prepping Blast table for easy join
``` bash
tr '|' '\t' < ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
> ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
head -1 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
```
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp P61915 ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
### 1.4.2 Could do some cool stuff in R here reading in table
``` r
bltabl <- read.csv("../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab", sep = '\t', header = FALSE)
spgo <- read.csv("https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/snaps/uniprot_table_r2023_01.tab", sep = '\t', header = TRUE)
datatable(head(bltabl), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(head(spgo), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(
left_join(bltabl, spgo, by = c("V3" = "Entry")) %>%
select(V1, V3, V13, Protein.names, Organism, Gene.Ontology..biological.process., Gene.Ontology.IDs)
)
```
 ``` r
summary(sequence_lengths_df)
```
## Length
## Min. : 102
## 1st Qu.: 519
## Median : 933
## Mean : 1338
## 3rd Qu.: 1617
## Max. :63597
``` r
# Calculate base composition
base_composition <- alphabetFrequency(sequences, baseOnly = TRUE)
# Convert to data frame and reshape for ggplot2
base_composition_df <- as.data.frame(base_composition)
base_composition_df$ID <- rownames(base_composition_df)
base_composition_melted <- reshape2::melt(base_composition_df, id.vars = "ID", variable.name = "Base", value.name = "Count")
# Plot base composition bar chart using ggplot2
ggplot(base_composition_melted, aes(x = Base, y = Count, fill = Base)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge", color = "black") +
labs(title = "Base Composition",
x = "Base",
y = "Count") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("A" = "green", "C" = "blue", "G" = "yellow", "T" = "red"))
```
``` r
summary(sequence_lengths_df)
```
## Length
## Min. : 102
## 1st Qu.: 519
## Median : 933
## Mean : 1338
## 3rd Qu.: 1617
## Max. :63597
``` r
# Calculate base composition
base_composition <- alphabetFrequency(sequences, baseOnly = TRUE)
# Convert to data frame and reshape for ggplot2
base_composition_df <- as.data.frame(base_composition)
base_composition_df$ID <- rownames(base_composition_df)
base_composition_melted <- reshape2::melt(base_composition_df, id.vars = "ID", variable.name = "Base", value.name = "Count")
# Plot base composition bar chart using ggplot2
ggplot(base_composition_melted, aes(x = Base, y = Count, fill = Base)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge", color = "black") +
labs(title = "Base Composition",
x = "Base",
y = "Count") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("A" = "green", "C" = "blue", "G" = "yellow", "T" = "red"))
```
 ``` r
# Count CG motifs in each sequence
count_cg_motifs <- function(sequence) {
cg_motif <- "CG"
return(length(gregexpr(cg_motif, sequence, fixed = TRUE)[[1]]))
}
cg_motifs_counts <- sapply(sequences, count_cg_motifs)
# Create a data frame
cg_motifs_counts_df <- data.frame(CG_Count = cg_motifs_counts)
# Plot CG motifs distribution using ggplot2
ggplot(cg_motifs_counts_df, aes(x = CG_Count)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, color = "black", fill = "blue", alpha = 0.75) +
labs(title = "Distribution of CG Motifs",
x = "Number of CG Motifs",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal()
```
``` r
# Count CG motifs in each sequence
count_cg_motifs <- function(sequence) {
cg_motif <- "CG"
return(length(gregexpr(cg_motif, sequence, fixed = TRUE)[[1]]))
}
cg_motifs_counts <- sapply(sequences, count_cg_motifs)
# Create a data frame
cg_motifs_counts_df <- data.frame(CG_Count = cg_motifs_counts)
# Plot CG motifs distribution using ggplot2
ggplot(cg_motifs_counts_df, aes(x = CG_Count)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, color = "black", fill = "blue", alpha = 0.75) +
labs(title = "Distribution of CG Motifs",
x = "Number of CG Motifs",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal()
```
 ## 1.2 Database Creation
### 1.2.1 Obtain Fasta (UniProt/Swiss-Prot)
``` bash
cd ../../data
curl -O https://ftp.uniprot.org/pub/databases/uniprot/current_release/knowledgebase/complete/uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz
mv uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
gunzip -k uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
```
### 1.2.2 Making the database
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/makeblastdb \
-in ../../data/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta \
-dbtype prot \
-out ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04
```
## 1.3 Running Blastx
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/blastx \
-query ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta \
-db ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04 \
-out ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
-evalue 1E-20 \
-num_threads 20 \
-max_target_seqs 1 \
-outfmt 6
```
``` bash
echo "First few lines:"
head -2 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
echo "Number of lines in output:"
wc -l ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
```
## First few lines:
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp|P61915|ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
## Parent=Peve_00000002 sp|Q569C3|UBP1_RAT 48.000 200 94 5 1287 703 407 601 1.43e-45 177
## Number of lines in output:
## 25243 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
## 1.4 Joining Blast table with annoations.
### 1.4.1 Prepping Blast table for easy join
``` bash
tr '|' '\t' < ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
> ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
head -1 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
```
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp P61915 ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
### 1.4.2 Could do some cool stuff in R here reading in table
``` r
bltabl <- read.csv("../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab", sep = '\t', header = FALSE)
spgo <- read.csv("https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/snaps/uniprot_table_r2023_01.tab", sep = '\t', header = TRUE)
datatable(head(bltabl), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(head(spgo), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(
left_join(bltabl, spgo, by = c("V3" = "Entry")) %>%
select(V1, V3, V13, Protein.names, Organism, Gene.Ontology..biological.process., Gene.Ontology.IDs)
)
```
## 1.2 Database Creation
### 1.2.1 Obtain Fasta (UniProt/Swiss-Prot)
``` bash
cd ../../data
curl -O https://ftp.uniprot.org/pub/databases/uniprot/current_release/knowledgebase/complete/uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz
mv uniprot_sprot.fasta.gz uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
gunzip -k uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta.gz
```
### 1.2.2 Making the database
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/makeblastdb \
-in ../../data/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04.fasta \
-dbtype prot \
-out ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04
```
## 1.3 Running Blastx
``` bash
/home/shared/ncbi-blast-2.11.0+/bin/blastx \
-query ../../data/Porites_evermanni_CDS.fasta \
-db ../../blastdb/uniprot_sprot_r2023_04 \
-out ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
-evalue 1E-20 \
-num_threads 20 \
-max_target_seqs 1 \
-outfmt 6
```
``` bash
echo "First few lines:"
head -2 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
echo "Number of lines in output:"
wc -l ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
```
## First few lines:
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp|P61915|ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
## Parent=Peve_00000002 sp|Q569C3|UBP1_RAT 48.000 200 94 5 1287 703 407 601 1.43e-45 177
## Number of lines in output:
## 25243 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab
## 1.4 Joining Blast table with annoations.
### 1.4.1 Prepping Blast table for easy join
``` bash
tr '|' '\t' < ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx.tab \
> ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
head -1 ../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab
```
## Parent=Peve_00000001 sp P61915 ACTPC_ACTTE 57.714 175 72 2 528 7 40 213 2.22e-58 184
### 1.4.2 Could do some cool stuff in R here reading in table
``` r
bltabl <- read.csv("../output/02-Peve-reference-annotation/Porites_evermanni_CDS-uniprot_blastx_sep.tab", sep = '\t', header = FALSE)
spgo <- read.csv("https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/snaps/uniprot_table_r2023_01.tab", sep = '\t', header = TRUE)
datatable(head(bltabl), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(head(spgo), options = list(scrollX = TRUE, scrollY = "400px", scrollCollapse = TRUE, paging = FALSE))
```
``` r
datatable(
left_join(bltabl, spgo, by = c("V3" = "Entry")) %>%
select(V1, V3, V13, Protein.names, Organism, Gene.Ontology..biological.process., Gene.Ontology.IDs)
)
```