Create and inspect alignment files. Visualize and capture “outside” graphics from programs outside of RStudio. Publish notebook in rpubs and provide link at top of code.
Look at Alignment Files using tview
Download alignment data
BAM files
Code
cd ../datacurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/scrubbed/120321-cvBS/19F_R1_val_1_bismark_bt2_pe.deduplicated.sorted.bamcurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/scrubbed/120321-cvBS/19F_R1_val_1_bismark_bt2_pe.deduplicated.sorted.bam.bai
Genome C. virginica (Eastern Oyster) FASTA files
Code
cd ../datacurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/data/Cvirg-genome/GCF_002022765.2_C_virginica-3.0_genomic.facurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/data/Cvirg-genome/GCF_002022765.2_C_virginica-3.0_genomic.fa.fai
Visualize with tview
Warning
Because tview is an interactive output directly in a Terminal window, you will want to run the following code in Terminal (not in a code chunk!)
In terminal change directory cd to the same directory as this code In my case, I typed cd assignments/code into Terminal
Then, copy and paste the following directly into Terminal:
You will get an output in Terminal that looks like this:
tview screenshot of aligned reads in each row below the reference genome (top row)
And you can navigate and query it using some special commands…. check out MORE HERE for details
Aligning WGS data and Visualizing in IGV
Curl C. gigas (Pacific Oyster) FASTQ files
Code
cd ../datacurl-O https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/C_gigas/F143n08_R2_001.fastq.gzcurl-O https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/C_gigas/F143n08_R1_001.fastq.gz
Curl C. gigas (Pacific Oyster) Genome files
Info
A .fa file ending typically indicates that the file contains DNA or protein sequence data in FASTA format. A .fa file may contain a single sequence or multiple sequences, and it can be generated from a variety of sources, such as genome sequencing data, transcriptome sequencing data, or protein sequence data.
Info
GTF (Gene Transfer Format): The GTF file format is a tab-delimited text file that contains information about gene structure, including the genomic coordinates of exons, introns, transcripts, and other features such as start and stop codons, reading frames, and gene names.The basic structure of a GTF file consists of one line per feature, with each line containing information about a specific genomic feature. The file typically includes information about the location, orientation, and other characteristics of the feature.GTF files are often used in conjunction with genomic sequence data to annotate genes and other genomic features, and they are used by a wide range of software tools for analysis and visualization of genomic data.
Code
cd ../datacurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.facurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.fa.faicurl-O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/GCF_902806645.1_cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.gtf
Look at GTF
Code
head ../data/GCF_902806645.1_cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.gtf
Build Index file with HISAT2
Info
The Index file output is actually 8 files! which end in *.index.{1-8}.ht2
This SAM file is 63.9GB and takes a long time to generate! If it takes too long, you can skip cheat and instead point to /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.sam
head /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.sam
Convert SAM to BAM
Warning
Again, you can skip, and point to /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.bam
Code
# Convert SAM to BAM, using 4 additional threads/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools view -@ 4 -bS\../output/F143_cgigas.sam > ../output/F143_cgigas.bam
Sort the BAM
Warning
Again, you can skip, and point to /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam
Code
# Sort the BAM file, using 4 additional threads/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools sort -@ 4 \../output/F143_cgigas.bam -o ../output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam
Index the sorted BAM file
Code
# Index the sorted BAM file (multi-threading is not applicable to this operation)/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools index \../output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam
Code
ls /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/*.bam
Use bcftools mpileup to generate a pileup in a (.txt) Binary Call Format file
Warning
Again, you can skip, and point to /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_mpileup_output.txt
bcftools mpileup is a command in the bcftools suite, which is a set of tools for variant calling and manipulating genomic variants. The mpileup command takes a set of sequence alignment files in BAM format and generates a pileup in the BCF format.
A pileup is a compact representation of the alignment of reads to a reference genome. For each position in the genome, the pileup shows a list of reads that overlap that position, along with the nucleotide at that position in each read. The pileup also includes quality scores for each read and statistics summarizing the distribution of nucleotides at that position.
The mpileup command is often used as a pre-processing step for variant calling, as it provides the information needed to call variants at each position in the genome. The resulting BCF file can be further processed with other bcftools commands, such as call, to generate a list of genomic variants.
Here I take the F143_mpileup_output.txt from the crabby-duck directory and use bcftools call to call variants, output variant sites, and store the results in a compressed Variant Call Format (.vcf) file in this directory output folder.
Here is what each bcftools call option used in the chunk above and below means:
-m: This option is used to specify the mode of variant calling. In this case, it sets the mode to “multiallelic-caller”, meaning it will try to call all possible alleles at a site.
-v: This option tells bcftools call to output only variant sites (sites where at least one sample has a non-reference allele).
-Oz: This option specifies the output format and compression. -Oz tells bcftools to output a compressed BCF file, which is a binary file format used for storing genomic variation data.
-c: option tells bcftools to use the Bayesian method to call genotypes, which takes into account the probability of observing the variant allele given the sequencing error rate and the sequencing depth.
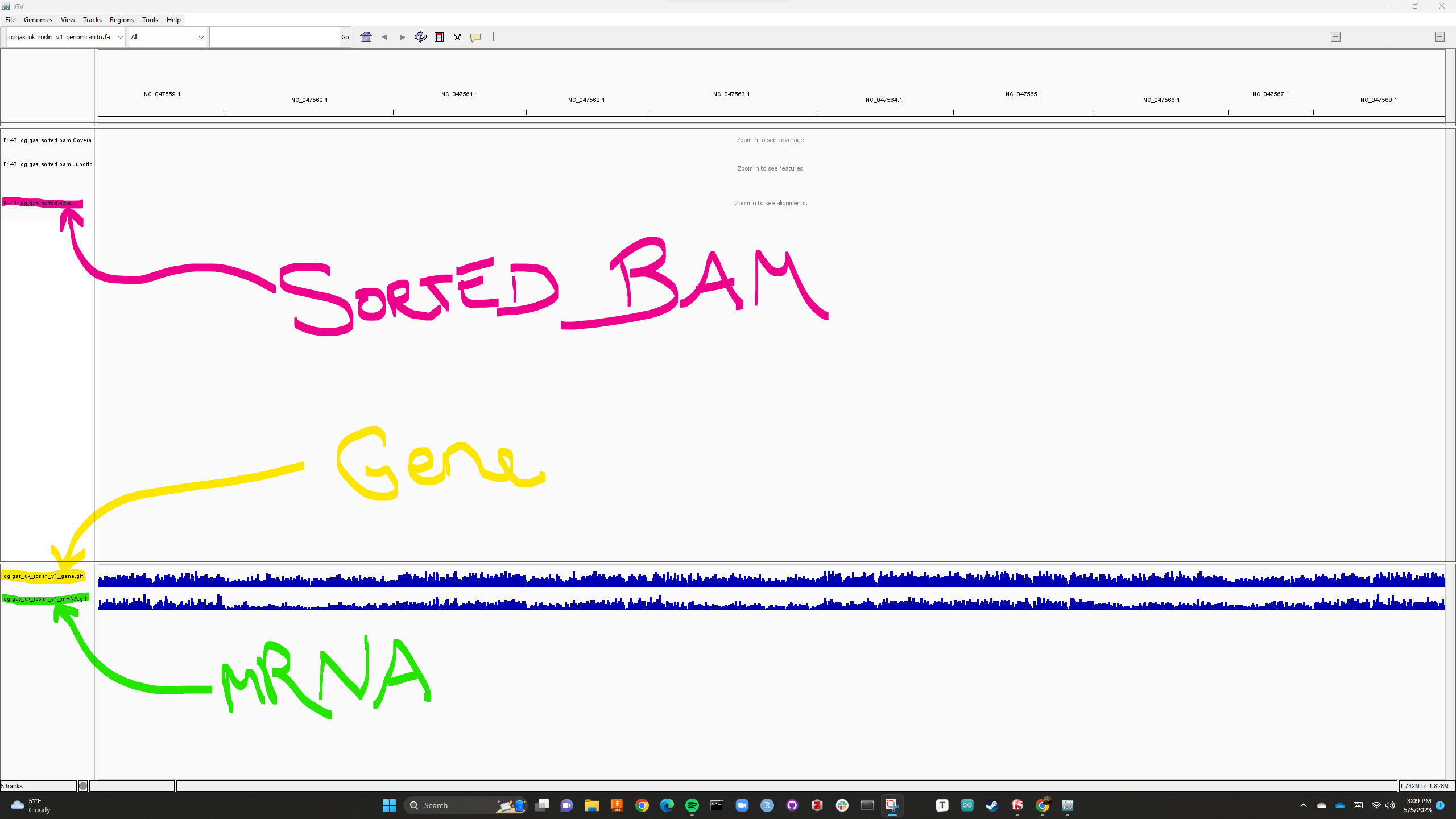
Integrated Gene Viewer with gene.gff and mRNA.gff feature tracks loaded, bam and vcf feature tracks still loading
Source Code
---title: "Visualize Alignments using `tview` and `Integrated Genome Viewer`"author: "Sarah Tanja"date: "`r format(Sys.time(), '%d %B, %Y')`" format: html: df-print: paged toc: true smooth-scroll: true link-external-icon: true link-external-newwindow: true code-fold: show code-tools: true code-copy: true highlight-style: arrow code-overflow: wrap theme: light: sandstone dark: vapor gfm: default---```{r setup, include=FALSE}knitr::opts_chunk$set(highlight =TRUE, # Highlight codeecho =TRUE, # Display code chunkseval =FALSE, # Evaluate code chunkswarning =TRUE, # Hide warningsmessage =TRUE, # Hide messagesfig.width =6, # Set plot width in inchesfig.height =4, # Set plot height in inchesfig.align ="center"# Align plots to the center )getwd()```Assignment Goals::: callout-infoCreate and inspect alignment files. Visualize and capture "outside" graphics from programs outside of RStudio. Publish notebook in rpubs and provide link at top of code.:::# Look at Alignment Files using `tview`## Download alignment data### BAM files```{r, engine='bash'}cd ../datacurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/scrubbed/120321-cvBS/19F_R1_val_1_bismark_bt2_pe.deduplicated.sorted.bamcurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/scrubbed/120321-cvBS/19F_R1_val_1_bismark_bt2_pe.deduplicated.sorted.bam.bai```### Genome C. virginica (Eastern Oyster) FASTA files```{r, engine='bash'}cd ../datacurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/data/Cvirg-genome/GCF_002022765.2_C_virginica-3.0_genomic.facurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-mox/data/Cvirg-genome/GCF_002022765.2_C_virginica-3.0_genomic.fa.fai```### Visualize with `tview`::: callout-warningBecause `tview` is an interactive output directly in a Terminal window, you will want to run the following code in Terminal (not in a code chunk!):::In terminal change directory `cd` to the same directory as this code In my case, I typed `cd assignments/code` into TerminalThen, copy and paste the following directly into Terminal:```{r, engine='bash'}/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools tview \../data/19F_R1_val_1_bismark_bt2_pe.deduplicated.sorted.bam \../data/GCF_002022765.2_C_virginica-3.0_genomic.fa```You will get an output in Terminal that looks like this: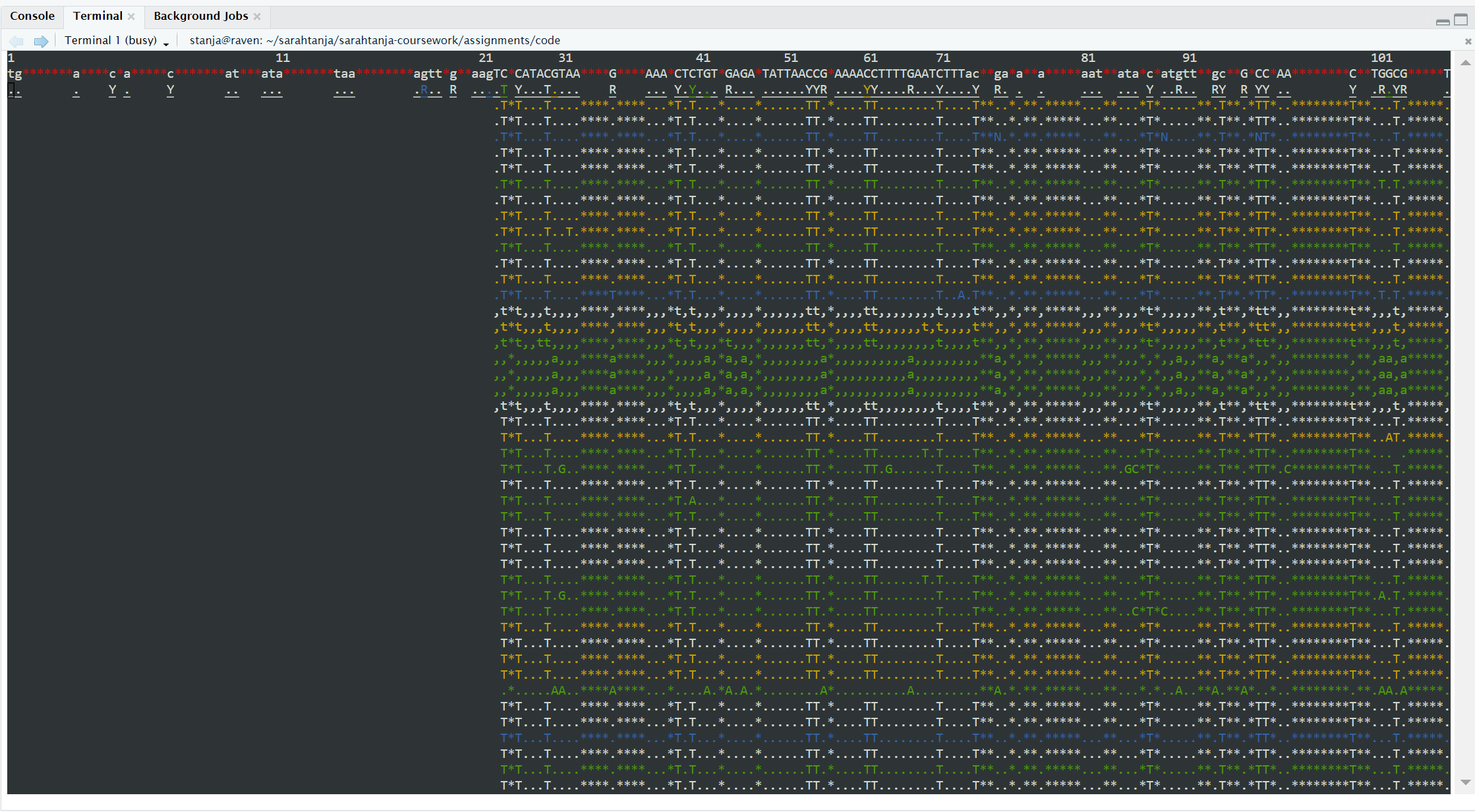And you can navigate and query it using some special commands.... check out [MORE HERE]() for details# Aligning WGS data and Visualizing in IGV### Curl C. gigas (Pacific Oyster) FASTQ files```{r, engine='bash'}cd ../datacurl -O https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/C_gigas/F143n08_R2_001.fastq.gzcurl -O https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/C_gigas/F143n08_R1_001.fastq.gz```### Curl C. gigas (Pacific Oyster) Genome files::: callout-infoA .fa file ending typically indicates that the file contains DNA or protein sequence data in FASTA format. A .fa file may contain a single sequence or multiple sequences, and it can be generated from a variety of sources, such as genome sequencing data, transcriptome sequencing data, or protein sequence data.:::::: callout-infoGTF (Gene Transfer Format): The GTF file format is a tab-delimited text file that contains information about gene structure, including the genomic coordinates of exons, introns, transcripts, and other features such as start and stop codons, reading frames, and gene names.The basic structure of a GTF file consists of one line per feature, with each line containing information about a specific genomic feature. The file typically includes information about the location, orientation, and other characteristics of the feature.GTF files are often used in conjunction with genomic sequence data to annotate genes and other genomic features, and they are used by a wide range of software tools for analysis and visualization of genomic data.:::```{r, engine='bash'}cd ../datacurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.facurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.fa.faicurl -O https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/GCF_902806645.1_cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.gtf```Look at GTF```{r, engine='bash'}head ../data/GCF_902806645.1_cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.gtf```### Build Index file with `HISAT2`::: callout-infoThe Index file output is actually **8 files!** which end in `*.index.{1-8}.ht2`:::```{r, engine='bash'}/home/shared/hisat2-2.2.1/hisat2-build \-f ../data/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.fa \../output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index```### Use Index file for Alignment, build the SAM file::: callout-warningThis SAM file is 63.9GB and takes a long time to generate! If it takes too long, you can skip cheat and instead point to `/home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.sam`:::```{r, engine='bash'}/home/shared/hisat2-2.2.1/hisat2 \-x ../output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index \-p 10 \-1 ../data/F143n08_R1_001.fastq.gz \-2 ../data/F143n08_R2_001.fastq.gz \-S ../output/F143_cgigas.sam```### Look at Human-Readable SAM file```{r, engine='bash'}head /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.sam```### Convert SAM to BAM::: callout-warningAgain, you can skip, and point to `/home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas.bam`:::```{r, engine='bash'}# Convert SAM to BAM, using 4 additional threads/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools view -@4-bS \../output/F143_cgigas.sam > ../output/F143_cgigas.bam```### Sort the BAM::: callout-warningAgain, you can skip, and point to `/home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam`:::```{r, engine='bash'}# Sort the BAM file, using 4 additional threads/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools sort -@4 \../output/F143_cgigas.bam -o ../output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam```### Index the sorted BAM file```{r, engine='bash'}# Index the sorted BAM file (multi-threading is not applicable to this operation)/home/shared/samtools-1.12/samtools index \../output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam``````{r, engine='bash'}ls /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/*.bam```## Use `bcftools mpileup` to generate a pileup in a (.txt) Binary Call Format file::: callout-warningAgain, you can skip, and point to `/home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_mpileup_output.txt`:::```{r, engine='bash'}/home/shared/bcftools-1.14/bcftools mpileup --threads 4--no-BAQ \--fasta-ref ../data/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.fa \../output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam > ../output/F143_mpileup_output.txt````bcftools mpileup` is a command in the bcftools suite, which is a set of tools for variant calling and manipulating genomic variants. The `mpileup` command takes a set of sequence alignment files in BAM format and generates a pileup in the BCF format.A pileup is a compact representation of the alignment of reads to a reference genome. For each position in the genome, the pileup shows a list of reads that overlap that position, along with the nucleotide at that position in each read. The pileup also includes quality scores for each read and statistics summarizing the distribution of nucleotides at that position.The `mpileup` command is often used as a pre-processing step for variant calling, as it provides the information needed to call variants at each position in the genome. The resulting BCF file can be further processed with other `bcftools` commands, such as `call`, to generate a list of genomic variants.Take a look at the pileup `F143_mpileup_output.txt````{r, engine='bash'}tail /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_mpileup_output.txt```Here I take the `F143_mpileup_output.txt` from the crabby-duck directory and use `bcftools call` to call variants, output variant sites, and store the results in a compressed Variant Call Format (.vcf) file in this directory output folder.```{r, engine='bash'}cat /home/shared/8TB_HDD_01/sr320/github/steven-crabby-duck/output/F143_mpileup_output.txt \|/home/shared/bcftools-1.14/bcftools call -mv -Oz \> ../output/F143_mpile.vcf.gz```Here is what each `bcftools call` option used in the chunk above and below means:-m: This option is used to specify the mode of variant calling. In this case, it sets the mode to "multiallelic-caller", meaning it will try to call all possible alleles at a site.-v: This option tells `bcftools call` to output only variant sites (sites where at least one sample has a non-reference allele).-Oz: This option specifies the output format and compression. -Oz tells bcftools to output a compressed BCF file, which is a binary file format used for storing genomic variation data.-c: option tells bcftools to use the Bayesian method to call genotypes, which takes into account the probability of observing the variant allele given the sequencing error rate and the sequencing depth.```{r, engine='bash'}/home/shared/bcftools-1.14/bcftools call \-v -c ../output/F143_mpile.vcf.gz \> ../output/F143_mpile_calls.vcf```When I run this chunk I get> Error: could not parse the input VCFDetails say `F143_mpile.vcf.gz` may be truncated# Visualize in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV)1. Download IGV software and install it on your local machine <https://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/download> - In my case, I downloaded "[IGV for Windows Java Included](https://data.broadinstitute.org/igv/projects/downloads/2.16/IGV_Win_2.16.1-WithJava-installer.exe)"2. Open IGV Viewer3. Load a Reference Genome: Go to `Genomes`\>`Load Genome from URL` and enter: <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/panopea/Cg-roslin/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.fa>:::callout-warningLoading the URL's in IGV does take time, this process is slow and requires patience:::4. Load a sorted BAM file and the BAM Index file: Go to `File`\>`Load from URL` and enter: - BAM file: - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/F143_cgigas_sorted.bam> - BAM Index file ... But there are 8 to choose from? Which one? - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.1.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.2.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.3.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.4.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.5.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.6.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.7.ht2> - <https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/seashell/bu-546/stanja/sarahtanja/sarahtanja-coursework/assignments/output/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_genomic-mito.index.8.ht2>5. Load a VCF file: Go to `File`\>`Load from URL` and enter: - <https://raw.githubusercontent.com/course-fish546-2023/sarahtanja-coursework/master/assignments/output/F143_mpile_calls.vcf>6. Load other feature tracks from [Roberts Lab Genomic Resources](https://robertslab.github.io/resources/Genomic-Resources/#crassostrea-gigas-oyster_v9) using `File`\>`Load from URL` : - cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_gene.gff: - <http://owl.fish.washington.edu/halfshell/genomic-databank/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_gene.gff> - cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_mRNA.gff: - <http://owl.fish.washington.edu/halfshell/genomic-databank/cgigas_uk_roslin_v1_mRNA.gff>